As the global push for carbon neutrality and the development of green industries continue, we aim to explore the opportunities and current challenges in China’s CCUS (Carbon Capture, Utilization, and Storage) industry, which is experiencing growth.
Table of Contents
What is CCUS
CCUS, or Carbon Capture, Utilization, and Storage, is a technology that involves capturing carbon dioxide (CO2) and utilizing it while also storing it. Initially, the technology began with CCS (Carbon Capture and Storage), which focused on capturing and directly storing carbon. However, challenges such as storage space limitations and the economic value of utilizing captured carbon led to the development of CCUS, combining both capture and utilization technologies.
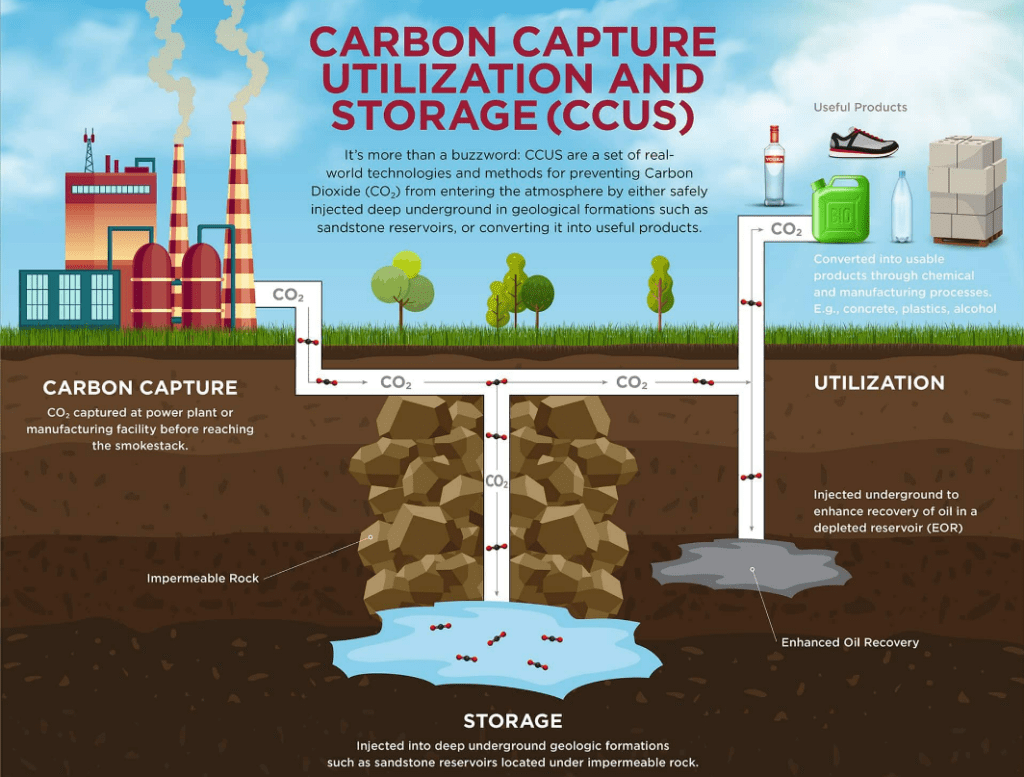
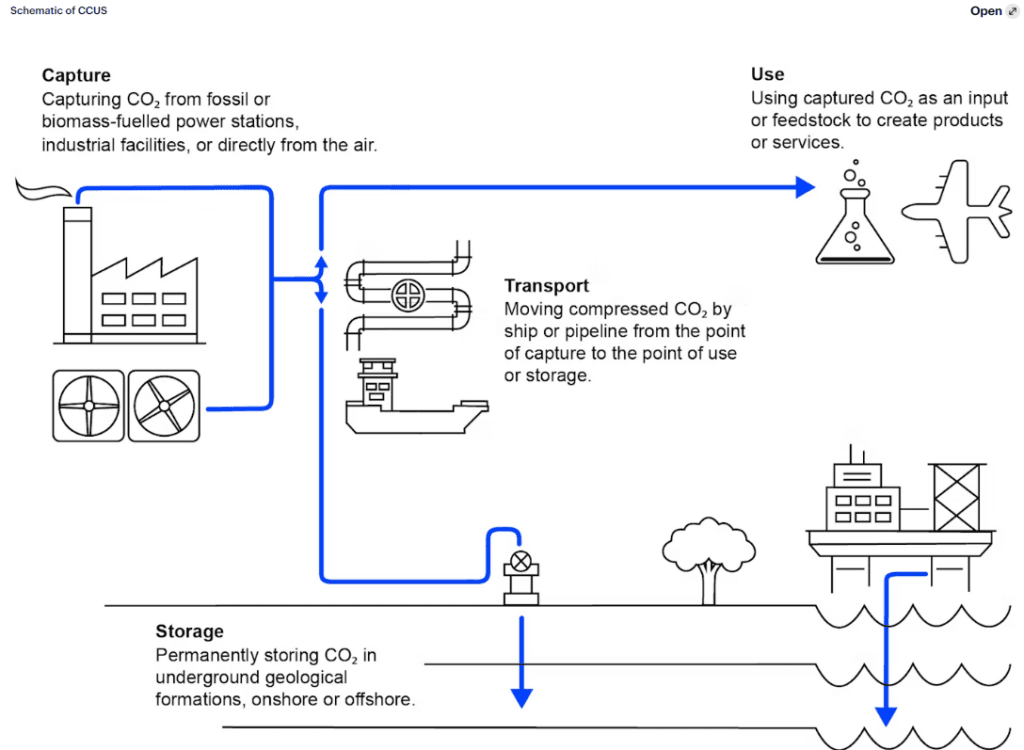
Source: IEA Homepage (https://www.iea.org/reports/ccus-in-clean-energy-transitions/a-new-era-for-ccus)
Trends in CCUS Investment in China
In June of this year, a pilot CCUS project with an annual capacity of 500,000 tons was launched at the CHN Energy power plant. This project captures carbon emissions from the largest coal-fired power plant in Asia. It marks a significant large-scale pilot project covering capture, utilization (specifically Enhanced Oil Recovery, injecting gases into oil reservoirs to enhance recovery), and storage for the entire industry.
China has invested in CCUS with plans for an annual capacity of one million tons in 2022 and an additional 700,000 tons in the first half of 2023. Moreover, there are plans for an additional expansion of around 2.4 million tons. Preliminary research for a massive offshore CCUS project of ten million tons is also underway.
Various individual company projects, such as Shanghai’s strategic coal power plant, Guanghui Energy’s project, Shanxi Coal Group’s deep saline aquifer storage project, and Huaneng Jingning Coal Power Plant’s CCUS project, are also in progress.
Expansion of CCUS Industry and Investment Opportunities
- CCUS plays a crucial role in achieving a nation’s carbon emission reduction goals. According to the [Annual Report on Carbon Capture, Storage, and Utilization in China] published in 2021, it is estimated that 10-18 billion tons of CO2 must be reduced through CCUS technology by 2060.
- The drive for carbon neutrality in the energy system presents opportunities for CCUS. According to the director of the Energy Research Institute at Peking University, Jin Zengjun, achieving carbon neutrality by 2060 requires fossil energy to constitute 40% of China’s energy mix. Utilizing CCUS to retrofit existing coal power plants allows for managing carbon emissions while benefiting from the cost advantages of coal-fired generation.
- Industries with significant CO2 emissions in processes like steel and cement are also expected to focus on CCUS for concentrated reduction efforts. Despite employing traditional methods like process optimization, efficiency improvements, and energy/raw material substitution, these industries are likely to continue emitting carbon. Therefore, CCUS adoption is seen as essential to achieve Net Zero.
Current Challenges
- The high cost of CCUS has been a constraint on large-scale commercialization. The current cost of CO2 capture for coal power plants using chemical absorption or post-combustion capture technologies is around RMB 300-450 per ton (approximately $54-81). Additionally, transportation costs by tanker lorries are reported to be around 0.9-1.4 RMB per ton-kilometer.
- There are also concerns about the practical effectiveness and utilization of captured CO2. The economic viability of CO2 utilization methods like EOR for petroleum and gas/carbon capture is questioned, as some applications (e.g., food, welding) have short isolation cycles, limiting significant carbon emission reductions.
- The industry acknowledges that the development of CCUS requires time and patience. Improvements in technology maturity, cost reductions in future potential areas such as membrane separation, filtering, and adsorption technologies, along with scale expansion, industrial network extension, and pipeline transportation (cheaper than road transport) are identified as avenues to reduce CCUS costs.
While CCUS is not yet a fully activated sector, it is an industry that various countries, including South Korea, are actively working on for carbon reduction and decarbonization efforts. The potential for growth and development in the future is considered high.
According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), the global CCUS market is projected to grow significantly, with substantial growth expected, particularly in North America.
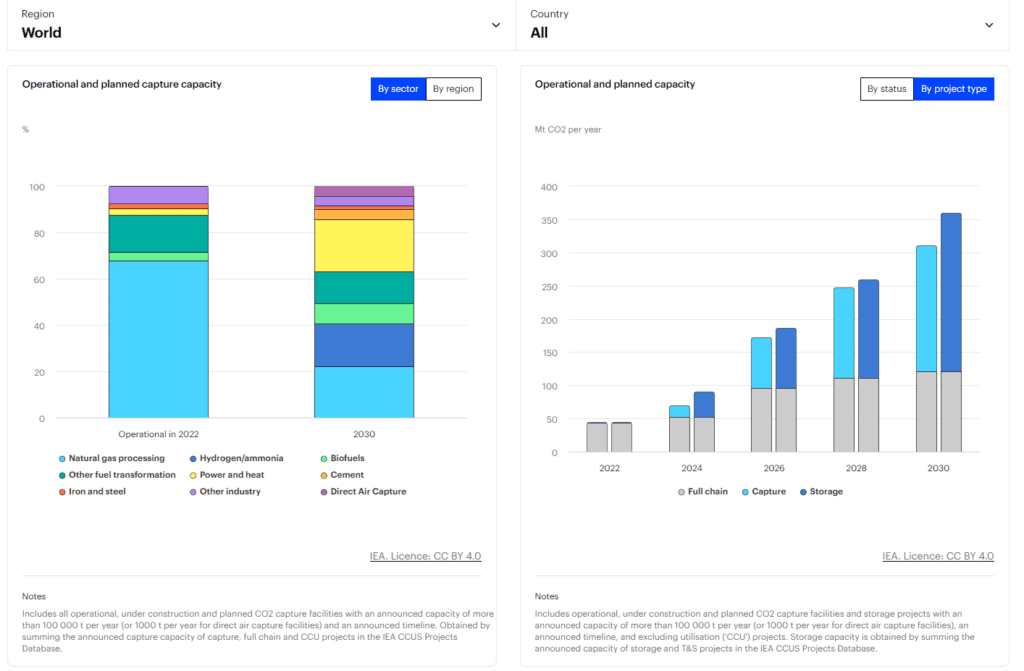
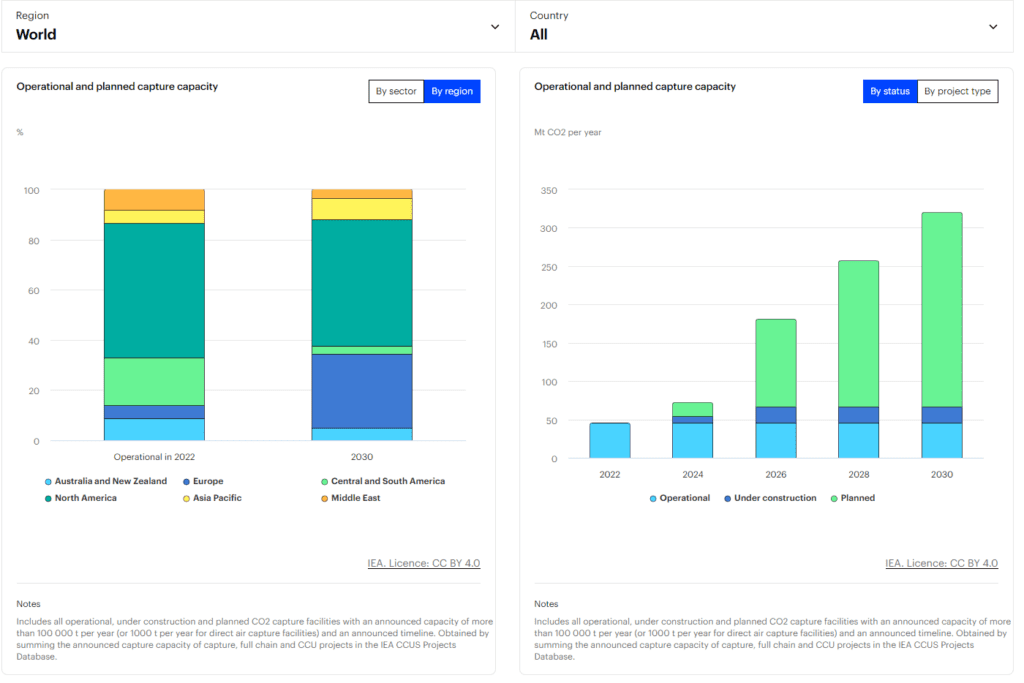
Source: IEA Homepage (https://www.iea.org/data-and-statistics/data-tools/ccus-projects-explorer)
[Reference] CO2 Compressor in the CCUS Value Chain
The carbon dioxide compressor (CO2 Compressor), a critical component in the CCUS value chain used for capture, transportation, liquefaction, and storage processes, is gaining attention. With an estimated market size of around $1.5 million in 2023 (currently approximately 75 CCUS projects worldwide), the CO2 compressor market is expected to grow explosively to a base of approximately $6 billion by 2027, driven by the growth of the CCUS market.
CO2 compressors are expected to be most widely used in the capture phase, followed by transportation pipelines and storage purposes.
If you have a particular interest in China, you may also want to consider referring to articles discussing China’s exchange rate policies.
